What is market research? It is one of the fundamental steps in starting a small business. Understanding your market is essential to identifying opportunities, gauging demand, and developing strategies to effectively reach your target audience. It can be an exciting endeavor full of potential, but it’s important to lay the right groundwork to ensure success.
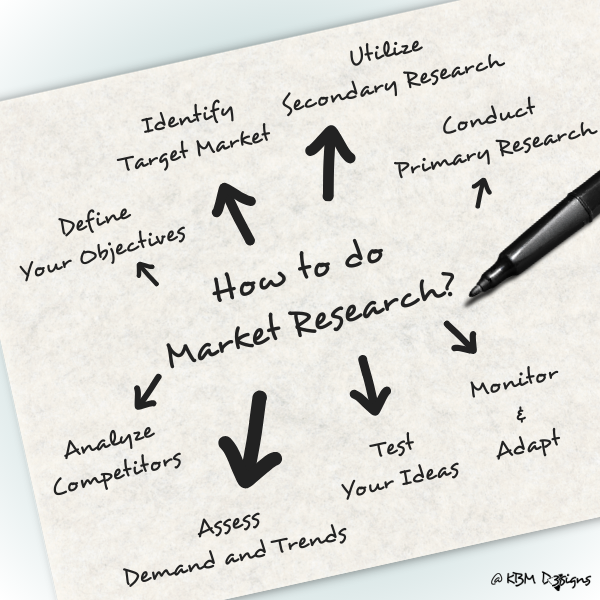
Article Content:
- A Comprehensive Guide On How To Conduct Market Research
- Defining Your Objectives Is The Crucial First Step
- Defining The Target Market, An Important Aspect In A Start-up
- Secondary Research, Gathers Information And Data By Other Sources
- Conducting Primary Research, Gathering Firsthand Data From The Source
- Analyzing Competitors, An Aspect Of Market Research Providing Valuable Insights
- Assessing Market Demand And Trends To Understand Market Dynamics
- Test Your Business Ideas Before Launching To Validate Assumptions
- Monitoring And Adapting, Components Of Market Research And Business Strategy
- Frequently Asked Questions About How To Do Market Research
1. A Comprehensive Guide On How To Conduct Market Research
Here’s a comprehensive 8-point guide to conducting market research when starting a small business:
1. Define Your Objectives:
Before diving into research, clearly outline your business objectives. Determine what you want to achieve with your business, whether it’s introducing a new product, targeting a specific demographic, or entering a niche market. Having clear goals will guide your research efforts and help you gather relevant information. Expand on business objectives…
2. Identify Your Target Market:
Define who your ideal customers are by considering factors such as demographics (age, gender, income level), psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests), and behavior (buying habits, preferences). This will help you tailor your products or services to meet their needs effectively. Expand on your target market…
3. Utilize Secondary Research:
Start by gathering existing data and information from secondary sources such as government statistics, industry reports, competitor websites, and market research studies. Analyze trends, market size, growth projections, and consumer preferences to gain insights into the broader market landscape. Expand on secondary research…
4. Conduct Primary Research:
Supplement secondary research with primary research to gather firsthand data specific to your business. This can include surveys, interviews, focus groups, or observation techniques. Ask questions to understand customer pain points, preferences, and buying behavior directly from your target audience. Expand on primary research…
5. Analyze Competitors:
Study your competitors to identify their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Analyze their products, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer reviews. This analysis will help you differentiate your business and identify areas where you can offer unique value. Expand on analyzing competitors…
6. Assess Demand and Trends:
Evaluate the demand for your products or services by analyzing consumer trends, industry forecasts, and economic indicators. Look for emerging trends, shifts in consumer behavior, and unmet needs that present opportunities for your business to capitalize on. Expand on assessing demand and trends…
7. Test Your Ideas:
Before fully launching your business, consider testing your ideas on a smaller scale. Conduct pilot studies, run focus groups, or offer prototypes to gather feedback and validate your assumptions. This iterative process will help refine your business concept and minimize risks. Expand on test your idea…
8. Monitor and Adapt:
Market research is an ongoing process. Stay vigilant and continuously monitor market trends, customer feedback, and competitor activities. Be prepared to adapt your strategies based on new insights and changing market conditions to stay competitive and relevant. Expand on monitor and adapt…
Ultimately, conducting effective market research is essential to the success of any small business. It allows you to make informed decisions and position your business for growth. You can do this by understanding your target market, assessing demand, and staying abreast of industry trends. Remember, market research is not a one-time activity. It is an ongoing process that should inform your business strategy at every stage of development.
2. Defining Your Objectives Is The Crucial First Step
Defining your objectives is the crucial first step in market research because it sets the direction for all your subsequent efforts.

Here’s a deeper dive into why this step is essential and how to go about it effectively:
Clarity and Focus:
Clearly outlining your business objectives provides clarity and focus. It helps you understand what you’re trying to accomplish with your business venture. Whether your goal is to increase revenue, expand into new markets, or solve a specific problem, having a clear objective ensures that your research efforts are aligned with your overarching goals.
Guiding Research Efforts:
Your objectives serve as a roadmap for your market research activities. They help you determine what information you need to gather, which markets to explore, and what questions to ask. Without well-defined objectives, your research efforts may lack direction and could result in collecting irrelevant or insufficient data.
Tailoring Strategies:
Different objectives require different strategies. For example, if your goal is to introduce a new product, your research may focus on understanding customer needs, assessing market demand, and evaluating competitors. On the other hand, if you aim to target a specific demographic, your research may delve into consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing habits within that demographic.
Setting Measurable Goals:
Defining objectives allows you to set measurable goals that you can track and evaluate over time. This could include metrics such as market share, customer acquisition rates, or revenue targets. By establishing clear benchmarks, you can gauge the success of your market research efforts and make data-driven decisions accordingly.
Adaptability and Flexibility:
While it’s important to have clear objectives, it’s also essential to remain flexible and adaptable. Market conditions may change, and new opportunities or challenges may arise along the way. Your objectives should be dynamic enough to accommodate shifts in the business landscape while still providing a guiding framework for your research endeavors.
Alignment with Stakeholders:
Clearly defined objectives ensure alignment with stakeholders such as investors, partners, and employees. When everyone understands the overarching goals of the business, they can contribute more effectively to the research process and collaborate towards achieving shared objectives.
Risk Mitigation:
Having well-defined objectives can help mitigate risks associated with starting a small business. By thoroughly researching market demand, competition, and consumer preferences, you can identify potential pitfalls early on and take proactive measures to mitigate them, minimizing the likelihood of costly mistakes.
To summarize, defining your objectives is the cornerstone of effective small business research. It provides clarity, focus, and direction to your research efforts. It ensures that you gather relevant information, tailor your strategies accordingly, and make informed decisions that are aligned with your overall goals.
3. Defining The Target Market, An Important Aspect In A Start-up
Identifying your target market is a critical step in the business planning process as it lays the foundation for understanding and effectively reaching your potential customers.

Here’s an elaboration on how to define your target market:
Demographics:
Demographics refer to quantifiable characteristics of your target audience. These include factors such as age, gender, income level, education level, occupation, marital status, and geographic location. By analyzing demographic data, you can gain insights into who your potential customers are and tailor your products or services to meet their specific needs. For example, if you’re selling luxury skincare products, your target market might be affluent individuals aged 30-50 living in urban areas.
Psychographics:
Psychographics delve deeper into the psychological and lifestyle attributes of your target audience. This includes their values, attitudes, beliefs, interests, hobbies, personality traits, and behavioral patterns. Understanding psychographics helps you segment your market based on shared characteristics and preferences. For instance, if you’re offering eco-friendly fashion accessories, your target market might be environmentally-conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Behavior:
Behavioral factors focus on how consumers interact with your products or services. This encompasses their buying habits, purchase frequency, brand loyalty, product usage, and decision-making processes. Analyzing consumer behavior allows you to identify patterns and trends that influence purchasing decisions. For example, if you’re launching a subscription-based meal kit service, your target market might consist of busy professionals seeking convenient and healthy meal solutions.
Tailoring Products or Services:
Once you’ve defined your target market based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior, you can tailor your products or services to meet their specific needs and preferences. This might involve customizing features, pricing structures, packaging designs, marketing messages, and distribution channels to resonate with your target audience. By aligning your offerings with the desires and expectations of your ideal customers, you can increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business success.
Overall, identifying your target market is an analysis of demographics, psychology, and behavior to define your ideal customer. With this knowledge, you can effectively tailor your products or services to meet their needs. This increases your chances of attracting and retaining loyal customers in a competitive market.
4. Secondary Research, Gathers Information And Data By Other Sources
Utilizing secondary research involves gathering information and data that have already been collected and published by other sources.

Here’s an elaboration on how to effectively utilize secondary research for market analysis:
Government Statistics:
Government agencies often collect and publish data on various aspects of the economy, demographics, and industries. This data can include population demographics, employment statistics, inflation rates, GDP growth, and more. By accessing government databases such as the Census Bureau, Bureau of Labor Statistics, or Department of Commerce, businesses can gain valuable insights into the overall economic landscape and specific market segments.
Industry Reports:
Industry reports compiled by research firms, trade associations, and market intelligence companies provide in-depth analysis and forecasts for specific industries. These reports typically cover market trends, competitive analysis, key players, regulatory issues, and growth projections. Accessing industry reports relevant to your business sector can help you understand market dynamics, identify opportunities, and assess competitive threats.
Competitor Websites:
Analyzing competitor websites can provide valuable information about their products, services, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer engagement efforts. Pay attention to product features, customer reviews, promotions, and any unique selling propositions (USPs) they highlight. By benchmarking against competitors, businesses can identify areas for differentiation and improvement to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Market Research Studies:
Market research studies conducted by research firms or academic institutions offer detailed insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns. These studies may include surveys, focus groups, or observational research conducted to understand specific market segments or industries. Analyzing market research studies can help businesses identify emerging trends, assess market size, and validate assumptions about target customers’ needs and preferences.
Analyzing Trends:
Look for recurring patterns or shifts in consumer behavior, technology adoption, regulatory changes, or market dynamics that may impact your industry. Trend analysis involves identifying both short-term fluctuations and long-term patterns to anticipate market developments and adapt strategies accordingly. By staying abreast of trends, businesses can proactively position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Market Size and Growth Projections:
Determine the size and growth potential of your target market by analyzing available data and projections. Understand factors driving market growth, such as population trends, economic indicators, technological advancements, or regulatory changes. Estimating market size and growth trajectories helps businesses assess the revenue potential and attractiveness of different market segments.
Consumer Preferences:
Investigate consumer preferences, tastes, and buying behavior through available research reports, surveys, or social media listening tools. Understand what drives purchasing decisions, product preferences, brand loyalty, and satisfaction levels among your target audience. This insight enables businesses to tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to better align with consumer needs and preferences.
Overall, leveraging secondary research sources provides businesses with a wealth of information to inform strategic decision-making, market positioning, and resource allocation. By systematically gathering and analyzing data from various secondary sources, businesses can gain valuable insights into the broader market landscape and make informed choices to drive success.
5. Conducting Primary Research, Gathering Firsthand Data From The Source
Primary research involves gathering first-hand data directly from the source. This could be your target audience or people directly involved in your business.
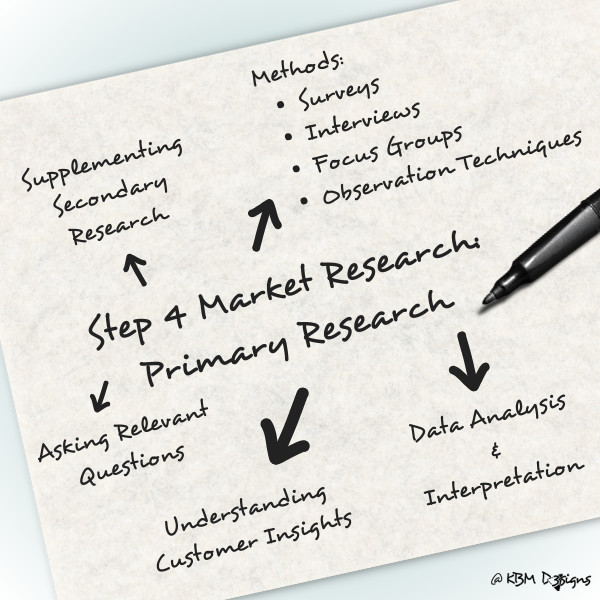
Here’s a detailed elaboration on conducting primary research:
Supplementing Secondary Research:
While secondary research provides valuable insights from existing data and sources, primary research complements this by offering specific, tailored information relevant to your business’s unique context. It helps validate or expand upon findings from secondary research and provides a deeper understanding of customer behaviors, preferences, and market dynamics.
Methods of Primary Research:
Primary research encompasses various methods to collect data directly from individuals or groups.
Common methods include:
- Surveys: Surveys involve administering structured questionnaires to a sample of respondents to gather quantitative data on their opinions, attitudes, and behaviors. Surveys can be conducted online, through email, phone calls, or in-person interviews.
- Interviews: Interviews entail engaging individuals in direct conversations to gather qualitative insights into their experiences, motivations, and perceptions. Interviews can be conducted one-on-one or in focus group settings, allowing for deeper exploration of topics.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a small group of individuals representing your target audience to discuss specific topics or products in a facilitated session. This method allows for interactive discussions and deeper insights into group dynamics and shared opinions.
- Observation Techniques: Observation involves systematically watching and recording behaviors, interactions, or events in natural settings. Observational research can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, product usage, and environmental factors influencing decision-making.
Asking Relevant Questions:
When conducting primary research, it’s essential to formulate clear, concise questions that address specific research objectives. Questions should be designed to elicit meaningful responses related to customer pain points, preferences, satisfaction levels, and buying behavior. Open-ended questions encourage respondents to provide detailed insights, while closed-ended questions facilitate quantitative analysis.
Understanding Customer Insights:
Primary research offers an opportunity to directly engage with your target audience and gain firsthand insights into their needs, motivations, and challenges. By actively listening to customer feedback and observing their behaviors, businesses can identify opportunities for product improvements, innovation, and targeted marketing strategies. Understanding customer pain points and preferences allows businesses to tailor their offerings to better meet customer needs and enhance overall satisfaction.
Data Analysis and Interpretation:
Once primary data is collected, it’s essential to analyze and interpret the findings to derive actionable insights. Quantitative data from surveys can be analyzed using statistical techniques to identify trends, correlations, and patterns, while qualitative data from interviews and focus groups require thematic analysis to uncover key themes and narratives. By synthesizing primary research findings with secondary research insights, businesses can make informed decisions and develop strategies aligned with customer needs and market trends.
By conducting primary research alongside secondary research, companies can gain first-hand insights directly from their target audience. Using a variety of research methodologies enables companies to gain valuable insights. These include insights into how consumers behave, what they prefer, and how they perceive the world around them.
6. Analyzing Competitors, An Aspect Of Market Research Providing Valuable Insights
Analysis of the competition is a critical aspect of market research. It provides valuable insight into the competitive landscape. Helping organizations develop effective strategies to differentiate themselves and gain market share.
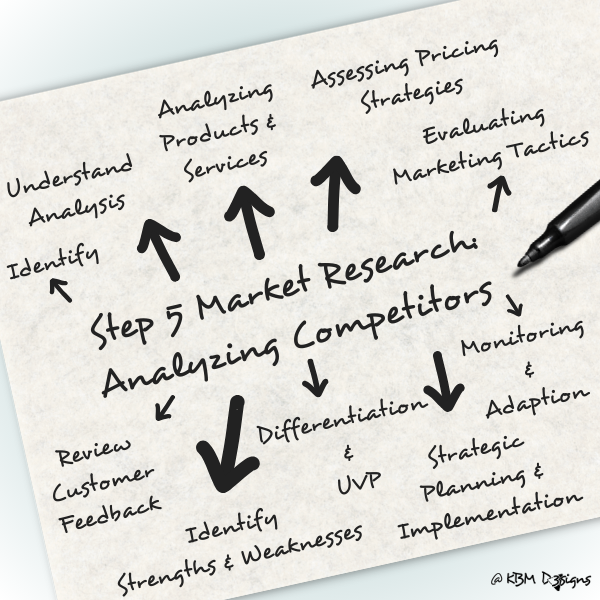
Here’s a detailed elaboration on how to analyze competitors:
Identifying Competitors:
Begin by identifying direct and indirect competitors operating in your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services to the same target audience, while indirect competitors may provide alternative solutions to fulfill similar customer needs.
Understanding Competitor Analysis:
Competitor analysis involves systematically evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and performance of competitors to gain a comprehensive understanding of their market positioning and competitive advantage.
Analyzing Products and Services:
Examine the products or services offered by competitors in terms of features, quality, pricing, and innovation. Identify any unique selling propositions (USPs) or competitive advantages they may have and assess how their offerings meet customer needs and preferences.
Assessing Pricing Strategies:
Analyze competitors’ pricing strategies to understand their pricing models, pricing levels, discounts, and promotions. Compare their pricing to your own pricing strategy and assess how competitive pricing influences customer perceptions and purchasing decisions.
Evaluating Marketing Tactics:
Study competitors’ marketing tactics and promotional activities across various channels, including digital marketing, advertising, social media, and content marketing. Analyze the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns, messaging, branding, and customer engagement strategies.
Reviewing Customer Reviews and Feedback:
Monitor customer reviews, feedback, and ratings for competitors’ products or services on review platforms, social media, and industry forums. Pay attention to common themes, complaints, and areas of satisfaction to identify areas for improvement or potential gaps in the market.
Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses:
Identify competitors’ key strengths and weaknesses based on your analysis of their products, pricing, marketing, and customer feedback. Assess their capabilities, resources, market share, and brand reputation to understand where they excel and where they may be vulnerable.
Differentiation and Unique Value Proposition (UVP):
Use the insights gathered from competitor analysis to identify opportunities for differentiation and develop a unique value proposition (UVP) for your own business. Highlight areas where you can offer superior value, address unmet customer needs, or provide a better customer experience compared to competitors.
Strategic Planning and Implementation:
Incorporate findings from competitor analysis into your strategic planning process to inform decision-making and resource allocation. Develop strategies and tactics that leverage your competitive strengths while addressing weaknesses and capitalizing on market opportunities.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
Competitor analysis is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor competitors’ actions, market trends, and changes in customer preferences to stay informed and adapt your strategies accordingly. Stay agile and be prepared to adjust your tactics to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
By conducting thorough competitor analysis, businesses can gain valuable insights into the competitive landscape, identify opportunities for differentiation, and develop effective strategies to position themselves for success in their target market.
7. Assessing Market Demand And Trends To Understand Market Dynamics
Demand and trend assessment is a critical component of market research. This allows businesses to better understand their current and future market dynamics. It also enables them to identify opportunities and make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and business expansion.
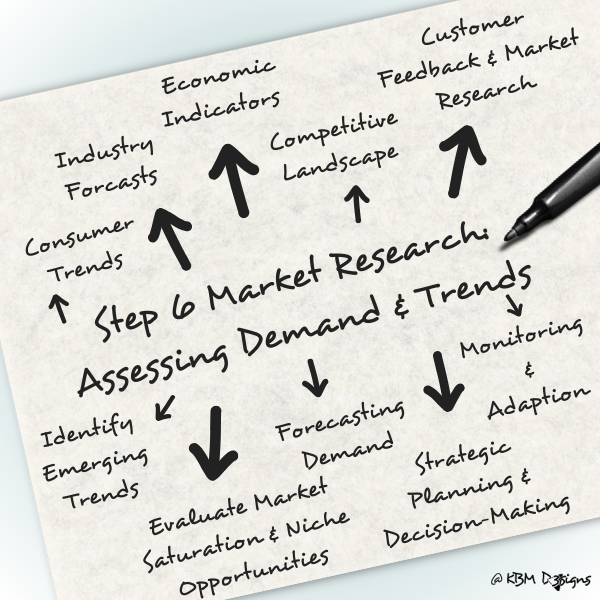
Here’s a detailed elaboration on how to assess demand and trends effectively:
Consumer Trends Analysis:
Start by analyzing consumer trends within your target market. This involves examining patterns of consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing habits. Look for shifts in consumer preferences, emerging lifestyle trends, and changes in buying patterns that may impact demand for your products or services.
Industry Forecasts:
Consult industry reports, market research studies, and forecasts specific to your industry or market segment. These sources provide valuable insights into market size, growth projections, and demand trends over time. Identify key drivers shaping the industry landscape and anticipate future market developments.
Economic Indicators:
Monitor relevant economic indicators that influence consumer spending and overall market demand. Factors such as GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, interest rates, and consumer confidence levels can impact purchasing power and consumer behavior. Assess how macroeconomic trends may affect demand for your products or services.
Competitive Landscape Analysis:
Evaluate the competitive landscape to understand how competitors are meeting market demand and addressing consumer needs. Analyze competitors’ product offerings, pricing strategies, marketing efforts, and market share to identify areas of opportunity or unmet needs that your business can capitalize on.
Customer Feedback and Market Research:
Gather feedback from existing and potential customers through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and social media interactions. Pay attention to customer preferences, pain points, and suggestions for improvement. Use market research techniques to gather quantitative and qualitative data on customer perceptions, satisfaction levels, and purchase intentions.
Identify Emerging Trends:
Keep abreast of emerging trends and innovations relevant to your industry or market niche. This may include technological advancements, changes in consumer preferences, new product trends, or regulatory developments. Identify emerging opportunities that align with your business’s strengths and capabilities.
Evaluate Market Saturation and Niche Opportunities:
Assess the level of market saturation within your industry and identify potential niche markets or underserved customer segments. Look for areas where competition is less intense or where your business can offer unique value propositions to differentiate itself and attract customers.
Forecasting Demand:
Use the insights gathered from demand analysis and trend assessment to forecast future demand for your products or services. Consider factors such as seasonality, market dynamics, and external influences when projecting sales volumes and revenue potential.
Strategic Planning and Decision-Making:
Incorporate findings from demand and trend analysis into your strategic planning process. Use this information to make informed decisions regarding product development, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, and market expansion initiatives. Tailor your strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
Demand and trends are dynamic and can change over time. Continuously monitor market conditions, consumer preferences, and industry developments to stay agile and responsive to changing demand patterns. Adapt your strategies and offerings as needed to remain competitive and meet evolving customer needs.
By systematically assessing demand and trends, businesses can gain valuable insight into market dynamics. They can also identify opportunities for growth. And they can develop strategies to position themselves for success in a competitive marketplace.
8. Test Your Business Ideas Before Launching To Validate Assumptions
Testing your ideas before fully launching your business is a prudent approach. It allows you to gather feedback, validate assumptions and refine your business concept. And do it before you commit significant time and resources.
Here’s a detailed elaboration on how to test your ideas effectively:
Pilot Studies:
Conduct pilot studies or small-scale trials to test your business concept in a controlled environment. This may involve offering your products or services to a limited group of customers or operating on a smaller scale to gauge interest and gather initial feedback. Pilot studies allow you to test feasibility, assess market demand, and identify potential challenges before scaling up.
Focus Groups:
Organize focus groups consisting of representative members of your target audience to gather qualitative feedback on your business idea. Facilitate discussions and ask participants open-ended questions to understand their perceptions, preferences, and concerns. Focus groups provide valuable insights into customer needs, preferences, and potential barriers to adoption.
Prototype Testing:
If you’re developing a new product or service, create prototypes or mock-ups to test functionality, usability, and appeal. Offer prototypes to a select group of users or customers for evaluation and feedback. Use their input to iterate and refine the product design, features, and user experience before finalizing the product for launch.
Market Surveys:
Design and administer surveys to gather quantitative data on customer preferences, purchase intent, and willingness to pay. Distribute surveys to a representative sample of your target market using online survey platforms, email campaigns, or social media channels. Analyze survey responses to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
A/B Testing:
Conduct A/B testing or split testing to compare different versions of your marketing materials, product features, pricing strategies, or website design. Divide your audience into two or more groups and expose them to different variations of your offerings. Measure and analyze the performance of each variation to determine which one resonates best with your target audience.
Iterative Refinement:
Use the feedback and insights gathered from testing to iteratively refine your business concept, product offering, or marketing strategy. Incorporate suggestions, address pain points, and make adjustments based on customer feedback and market trends. Iterate on your ideas until you achieve a viable and compelling value proposition.
Risk Mitigation:
Testing your ideas on a smaller scale helps mitigate risks associated with launching a new business or introducing a new product/service. By validating assumptions and gathering real-world feedback early in the process, you can identify and address potential pitfalls before they escalate into costly mistakes.
Learning and Adaptation:
Treat the testing phase as a learning opportunity to gather valuable insights about your target market, customer preferences, and competitive landscape. Be open to feedback, embrace experimentation, and be willing to adapt your approach based on what you learn during the testing process.
Data-Driven Decision Making:
Base your decisions on data and evidence collected through testing rather than assumptions or intuition alone. Use quantitative and qualitative data to inform strategic decisions, prioritize initiatives, and allocate resources effectively.
Continuous Improvement:
Testing is an ongoing process that doesn’t end with the launch of your business. Continuously gather feedback, monitor performance metrics, and iterate on your offerings to stay responsive to customer needs and market dynamics over time.
You can validate assumptions, refine your business concept, and increase the likelihood of success by testing your ideas on a smaller scale. Testing allows you to mitigate risk. It can also help you optimize resources and ensure that what you offer resonates with your audience.
9. Monitoring And Adapting, Components Of Market Research And Business Strategy
Monitoring and adapting are essential components of successful market research and business strategy.
Here’s a detailed elaboration on how to effectively monitor and adapt based on market research insights:
Continuous Monitoring:
Market research is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Stay vigilant by continuously monitoring market trends, consumer behavior, and industry developments. Utilize various sources of information such as industry reports, market surveys, social media monitoring, customer feedback channels, and competitor analysis to stay informed.
Stay Updated on Market Trends:
Keep abreast of emerging trends, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifts in consumer preferences that may impact your industry or market segment. Regularly scan industry publications, attend conferences, and engage with industry experts to stay updated on the latest developments.
Gather Customer Feedback:
Actively seek feedback from customers through surveys, reviews, feedback forms, and social media interactions. Pay attention to customer complaints, suggestions, and testimonials to gain insights into their experiences, preferences, and pain points. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance the customer experience.
Monitor Competitor Activities:
Keep a close eye on competitor activities, including product launches, marketing campaigns, pricing changes, and customer engagement strategies. Analyze competitor strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning to identify opportunities and threats. Benchmark your performance against competitors to assess your relative market position.
Data Analysis and Interpretation:
Analyze market research data and interpret insights to identify patterns, trends, and actionable opportunities. Use quantitative analysis techniques to crunch numbers and identify statistical trends, while qualitative analysis methods can help uncover deeper insights from customer feedback and qualitative data sources.
Adaptation and Strategy Adjustment:
Be prepared to adapt your strategies based on new insights and changing market conditions. If market trends shift or customer preferences evolve, adjust your product offerings, marketing messages, pricing strategies, or distribution channels accordingly. Remain agile and responsive to emerging opportunities and threats in the marketplace.
Iterative Improvement:
Treat market research and strategy adaptation as an iterative process of continuous improvement. Test new ideas, measure their impact, and iterate based on feedback and performance data. Embrace experimentation and be willing to pivot your strategies based on what works best for your business and your target audience.
Strategic Decision Making:
Base strategic decisions on data-driven insights rather than intuition or guesswork. Use market research findings to inform strategic planning, resource allocation, and prioritization of initiatives. Align your business goals and strategies with market realities to maximize your chances of success.
Remain Customer-Centric:
Keep the needs and preferences of your customers at the forefront of your decision-making process. Continuously seek ways to enhance the value proposition and customer experience to maintain customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Regular Review and Adjustment:
Establish regular review cycles to assess the effectiveness of your strategies and make adjustments as needed. Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and track performance over time. Use performance metrics to evaluate the impact of your actions and refine your approach accordingly.
By continuously monitoring market trends, customer feedback, and competitor activity. And by adapting your strategies based on new insights, you can stay competitive. Your business will remain relevant and responsive to the dynamic nature of the marketplace. This iterative approach to market research and strategy adaptation is essential for long-term business success and growth.
-

How To Choose A Life Coach Business Card Template
Read the post …: How To Choose A Life Coach Business Card Template -

What Is A Gift Voucher? An SMB Offline Marketing Perspective
Read the post …: What Is A Gift Voucher? An SMB Offline Marketing Perspective -

What is a Planner? A Small Business Perspective
Read the post …: What is a Planner? A Small Business Perspective
10. Frequently Asked Questions About How To Do Market Research
Market research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including its size, trends, competition, and customer preferences. It’s important for businesses because it helps them make informed decisions, understand their target audience, identify opportunities, and minimize risks.
There are two main types of market research: primary research and secondary research. Primary research involves collecting firsthand data directly from the source, while secondary research involves analyzing existing data and information collected by others.
Primary market research can be conducted through methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, observation, and experiments. These methods allow businesses to gather firsthand insights from their target audience about their preferences, behaviors, and needs.
Secondary market research sources include government publications, industry reports, academic journals, market research firms, trade associations, and online databases. These sources provide valuable data and information that businesses can use to understand market trends, competitors, and consumer behavior.
Identifying your target market involves defining the characteristics of your ideal customers, such as demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (lifestyle, interests), and behavior (buying habits, preferences). Conducting market research helps businesses pinpoint their target audience more effectively.
Analyzing competitors involves studying their strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, products/services, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer feedback. This analysis helps businesses understand their competitive landscape and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Assessing demand and trends involves analyzing consumer behavior, industry forecasts, economic indicators, and competitor activities. By monitoring market trends and consumer preferences, businesses can identify emerging opportunities and potential areas for growth.
Testing ideas before fully launching a business allows entrepreneurs to gather feedback, validate assumptions, and refine their business concept. It helps minimize risks, optimize resources, and increase the likelihood of success once the business is launched.
Monitoring and adapting market research strategies involve staying vigilant, continuously gathering insights from market trends, customer feedback, and competitor activities. Businesses should be prepared to adjust their strategies based on new insights and changing market conditions to stay competitive and relevant.
Common challenges in market research include limited budgets, accessing reliable data, defining a clear research objective, interpreting data accurately, and staying updated on evolving market trends. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, resource allocation, and leveraging the right tools and methodologies.
-

What Is A Brand Partnership? – A Small Business Perspective
Read the post …: What Is A Brand Partnership? – A Small Business Perspective -

What Are Business Objectives?” Perspective Of A Small Business
Read the post …: What Are Business Objectives?” Perspective Of A Small Business -

What Is A Focus Group Market Research? – SMB Perspective
Read the post …: What Is A Focus Group Market Research? – SMB Perspective


